Use case : Kidney transplant
Kidney rejection transplantation
Graft rejection constitutes the main challenge for kidney transplantation. Patient’s immune system attacks the foreign kidney, resulting in organ damages and impairs its physiological functions.
Kidney graft rejection is a common problem with a frequency of 8% the first-year and up to 30-40% 10 years after transplantation.


Providing a correct diagnosis of kidney transplant rejection remains a challenge and requires invasive technologies
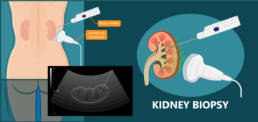
Kidney biopsy is the gold-standard method to put a diagnosis of kidney transplant rejection. This medical act consists of taking a small piece of tissue of the transplanted kidney to determine the presence of lesions, their types and confirm a rejection episode. Like any surgical procedure, it can lead to serious complications (10 to 15% of cases), and is therefore not used routinely.
Benefit of monitoring damaged kidney cells during an episode of transplant rejection
Depending on the kidney cells damaged during the rejection episode, the kidney failure will be different and its medical management also. Kidney failure can be classified into 4 categories : Fibrosis, vascular, tubular and glomerular.
A kidney biopsy has to be performed to put the precise diagnosis of the kidney failure during a rejection episode and propose an optimized therapy.
Rein
Kidney wall fibroblastic cells
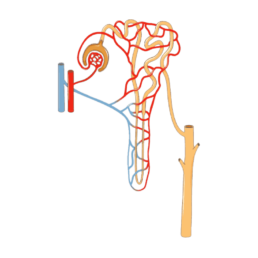
Nephron
Distal and proximal tubular cells
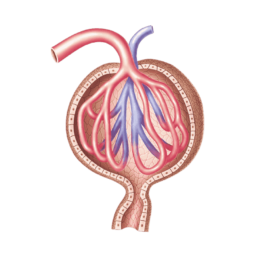
Glomerular
Glomerular cells (endothelial, epithelial, mesanglial, podocyte cells)
Kidney transplant patient care pathway
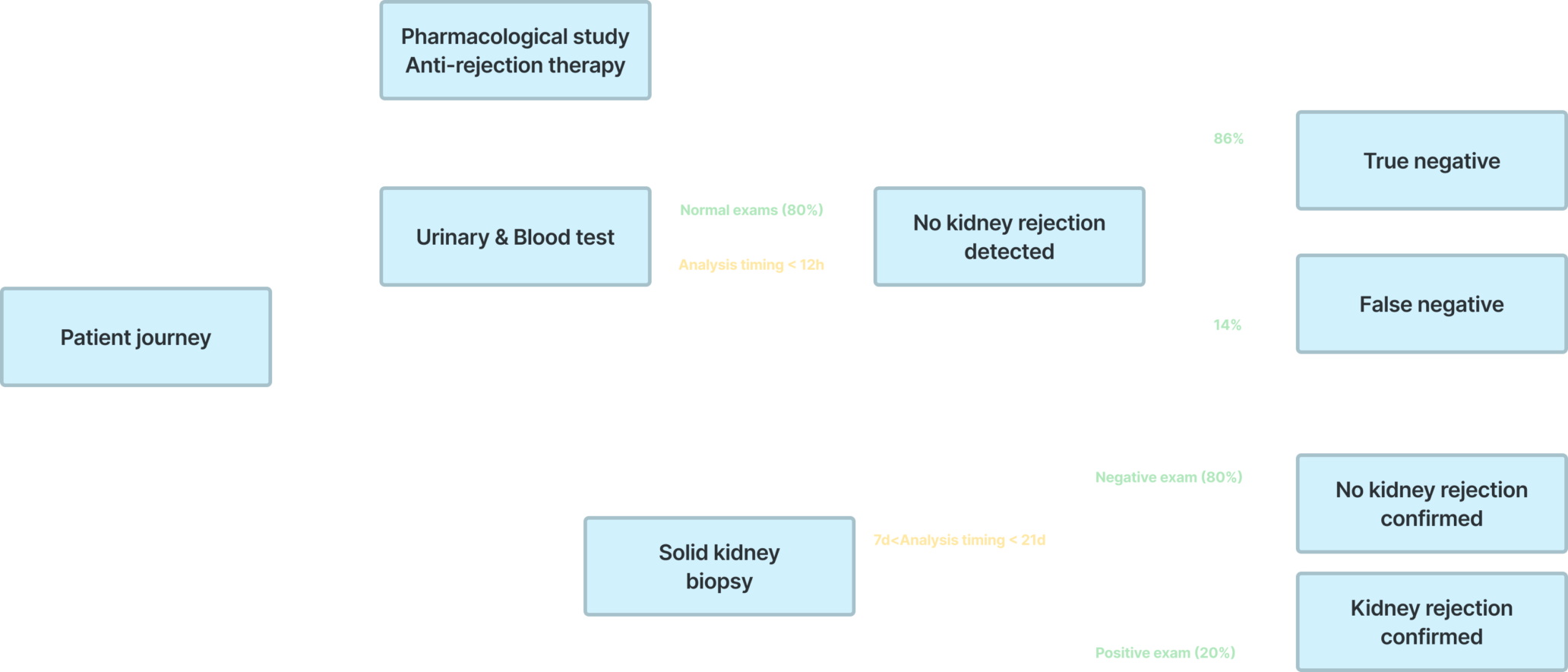
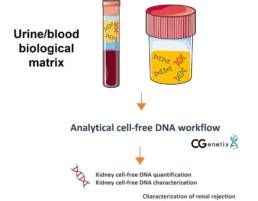
Urinary and blood
Urinary and blood test consists in quantifing biomarkers reflecting the functionality of the kidney (creatinine, Glomerular filtration rate…). They are performed at different frequency according to standardized guidelines :
- 2–3 times weekly for the first month after transplantation
- 1–2 times weekly for months 2–3
- Every 2–4 weeks for months 4–6
- Every 4–6 weeks for months 6–12
- 3–6 monthly thereafter
Pharmacological study Anti-rejection therapy
Pharmacodynamic of the anti-rejection drug is assessed according to standardized guidelines :
- 2–3 times weekly for the first month after transplantation
- 1–2 times weekly for months 2–3
- Every 2–4 weeks for months 4–6
- Every 4–6 weeks for months 6–12
- 3–6 monthly thereafter
Solid kidney biopsy
Kidney biopsy is the gold standard for the diagnostic of kidney graft rejection.
This analysis consists in quantifying, at cellular level, kidney lesions and analyzing immune cells and anti-HLA antibodies infiltrating the kidney graft
Solid kidney biopsy is performed at least one time during the first year (screening biopsy) and for each suspicious urinary & blood tests (up to 2-3 biopsies for patients facing a kidney biopsies)
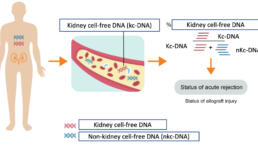
1° During a rejection episode, kidney cell-free DNA are released from dying kidney cells into the bloodstream of patients and diluted into non-kidney cell-free DNA